Financial decisions are an integral part of daily life, and instilling financial literacy in children has never been more critical.
Teaching kids about money management from a young age not only equips them with essential life skills but also lays the foundation for a secure financial future.
Here are some effective strategies for parents to help their children develop financial literacy:


Start Early:
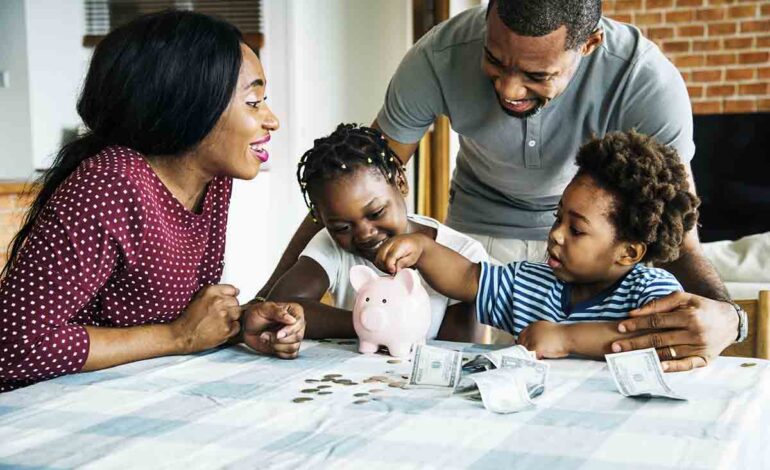
Financial education should begin as early as possible. Even preschoolers can grasp basic concepts like the value of money and the difference between wants and needs. Use everyday opportunities, such as grocery shopping or saving coins in a piggy bank, to introduce these concepts in a fun and interactive way.
Make it Relevant:
Connect financial lessons to real-life situations that children can relate to. For example, involve them in budgeting for a family vacation or saving for a special toy. By tying financial concepts to their own experiences, children are more likely to understand and retain the information.
Set a Good Example:
Children learn by observing their parents’ behavior. Model responsible financial habits, such as budgeting, saving, and avoiding impulse purchases. Let them see you comparing prices, making informed spending decisions, and prioritizing savings goals. Your actions speak louder than words when it comes to teaching financial literacy.
Use Allowance as a Teaching Tool:
Consider giving children a regular allowance to manage. Encourage them to divide their allowance into different categories, such as saving, spending, and giving. This hands-on experience helps children learn the value of budgeting and delayed gratification. Allow them to make mistakes and learn from them in a safe environment.
Introduce Basic Concepts:
As children grow older, gradually introduce more complex financial concepts, such as earning interest, managing debt, and investing. Use age-appropriate resources, such as books, games, or online simulations, to explain these concepts in an engaging manner. Encourage questions and open discussions about money matters.
Foster Entrepreneurial Spirit:
Encourage children to explore entrepreneurial ventures, such as setting up a lemonade stand or selling handmade crafts. These experiences teach valuable lessons about earning income, marketing products, and managing expenses. They also nurture creativity, resilience, and problem-solving skills.
Teach the Value of Giving:
In addition to saving and spending, emphasize the importance of giving back to others. Encourage children to donate a portion of their allowance or volunteer their time to charitable causes. Helping others not only cultivates empathy and generosity but also reinforces the idea that money can be a force for positive change.
Monitor Progress and Adjust:
Keep track of your child’s financial activities and progress over time. Offer guidance and support as needed, but also allow them to take ownership of their financial decisions. Adjust your approach based on their individual interests, strengths, and learning styles.
Emphasize Long-Term Goals:
Help children understand the concept of long-term financial goals, such as saving for college, buying a car, or starting a business. Teach them the importance of setting goals, creating a plan to achieve them, and staying disciplined along the way. Encourage them to dream big and work hard to turn their aspirations into reality.
Celebrate Milestones:
Celebrate milestones and achievements along the financial literacy journey. Whether it’s reaching a savings goal, making a wise spending decision, or starting their first investment account, acknowledge and praise their efforts. Positive reinforcement reinforces good habits and motivates children to continue learning and growing.
Teaching financial literacy to children is a valuable investment in their future success and well-being. With patience, consistency, and a supportive environment, every child can become financially savvy and confident in managing their money.
3.5